Boost Your Brainpower with Binaural Beats: The Science-Backed Tool for Sharper Memory and Focus
Studies have shown that listening to these specific sound frequencies can boost memory and attention by up to 30%.
What if I told you that putting on headhpones and listening to a very specific set of different frequences in each ear could genuinely sharpen your mind?
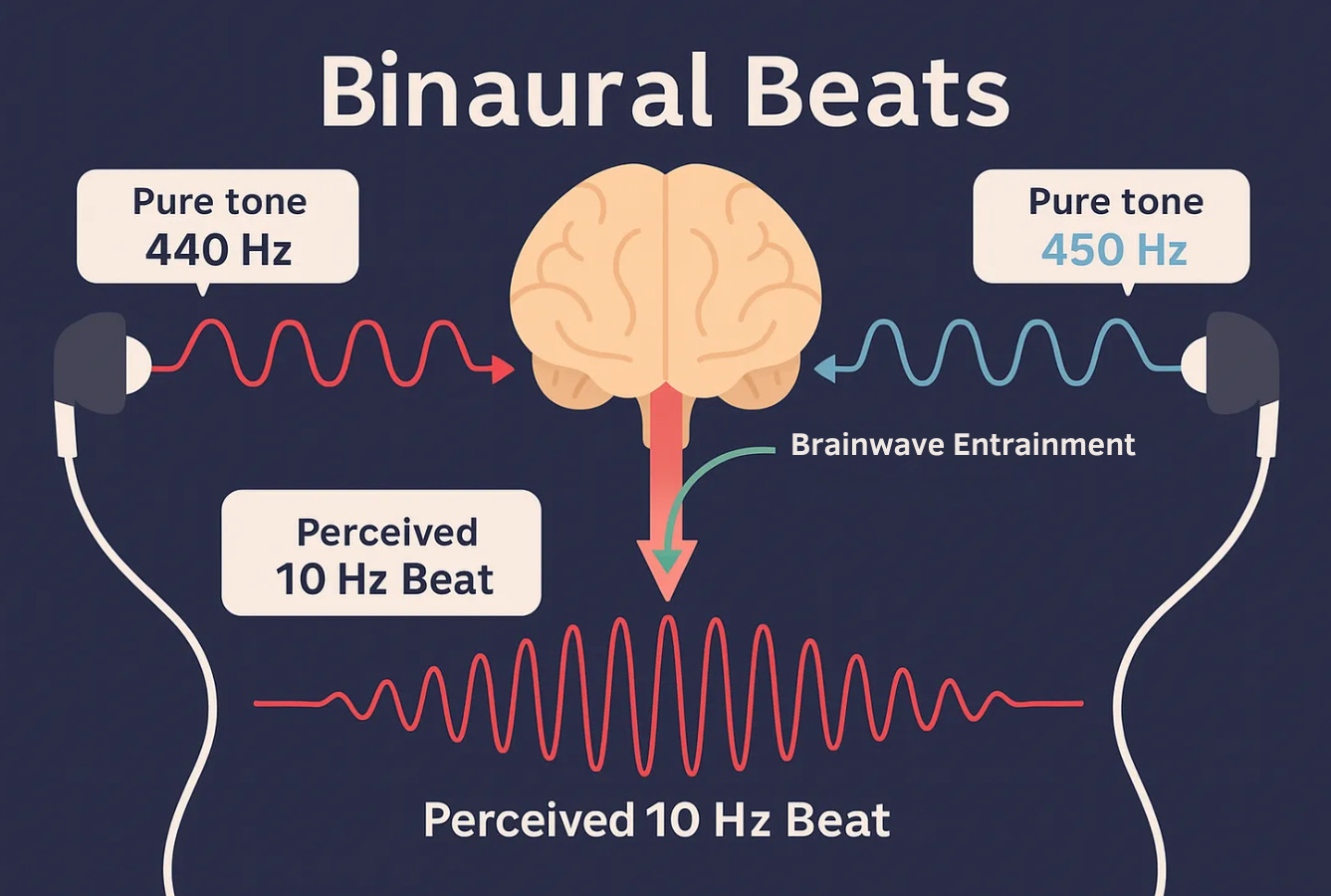
"Binaural beats" are auditory illusions created when each ear hears slightly different tones. And emerging evidence suggests they might hold the key to substantially improving memory and attention. By causing your brain to perceive a rhythmic "beat," binaural beats can synchronize your brainwaves. This has the potential to enhance memory, attention, and mental clarity. But not all beats are equal. Choosing the correct frequency is critical.
Quick Summary: Key Insights from Recent Studies
Memory Improvement: 20 Hz (beta frequency) binaural beats increased memory recall by up to 27% compared to white noise.
Attention and Fatigue Management: A single 12-minute session of 14 Hz (beta) beats completely prevented a 30% attention loss after intense mental activity, whereas other methods, like mindfulness for beginners, led to significant declines.
Frequency Matters: Only specific frequencies have benefit, and some may even cause harm. Using the exact right frequencies is critical.
Why and How Do Binaural Beats Work?
Beta binaural beats appear to stabilize brain regions critical for attention, memory, and executive functioning, such as the frontal and hippocampal areas. This neural stability likely underpins improvements seen in memory encoding and sustained attention.
Understanding Binaural Beats: A Fascinating Phenomenon
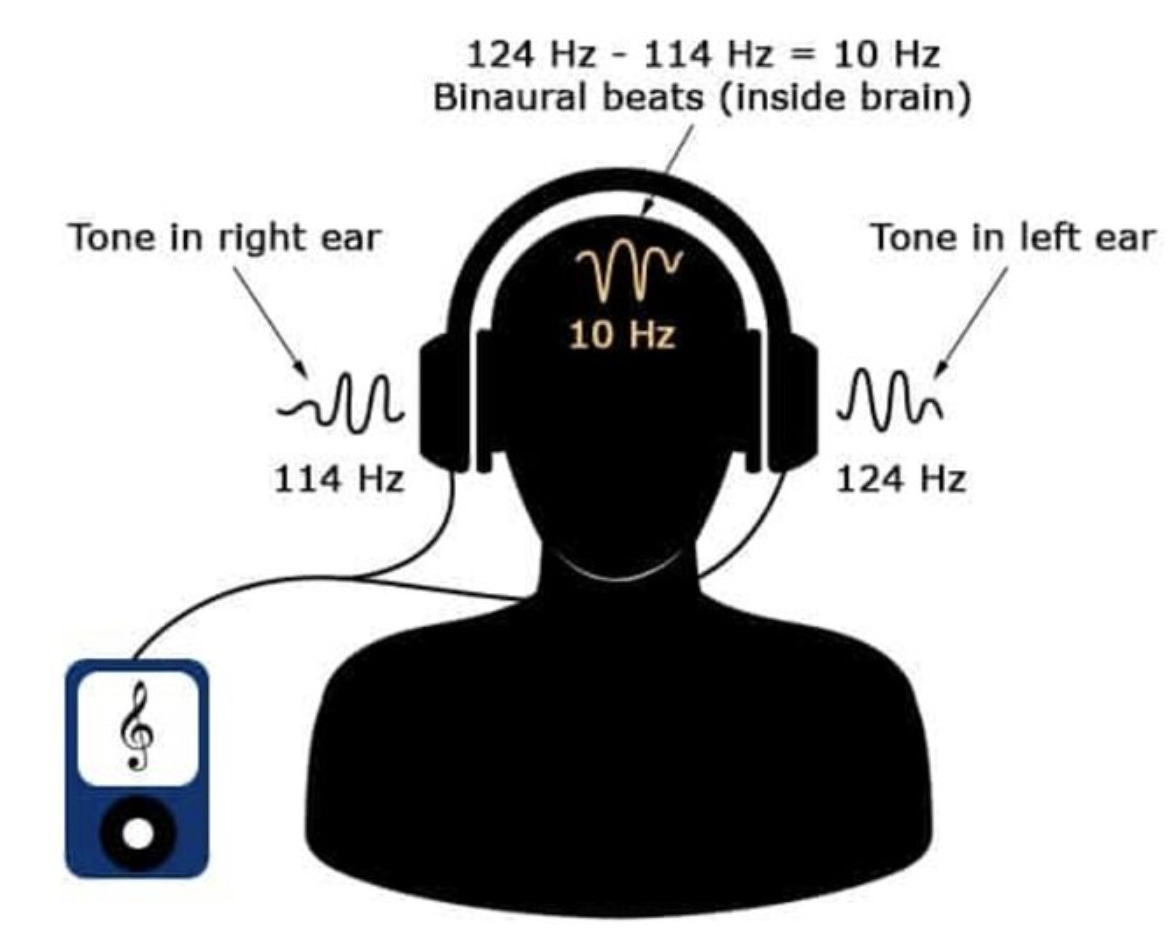
Binaural beats occur when your left and right ears receive two slightly different tones. Your brain reconciles this difference, creating a third, "phantom" beat that you perceive as a rhythmic pulse. This rhythmic pulse can synchronize your brain’s electrical activity. This is a process known as neural entrainment. Different frequencies of binaural beats correspond to different brain states:
Beta (12-30 Hz): Enhances alertness, concentration, problem-solving abilities.
Theta (4-7 Hz): Associated with relaxation, daydreaming, and meditation.
Could this synchronization measurably improve real-world cognitive tasks?
Study 1: Preservation of Attention Under Exhaustion
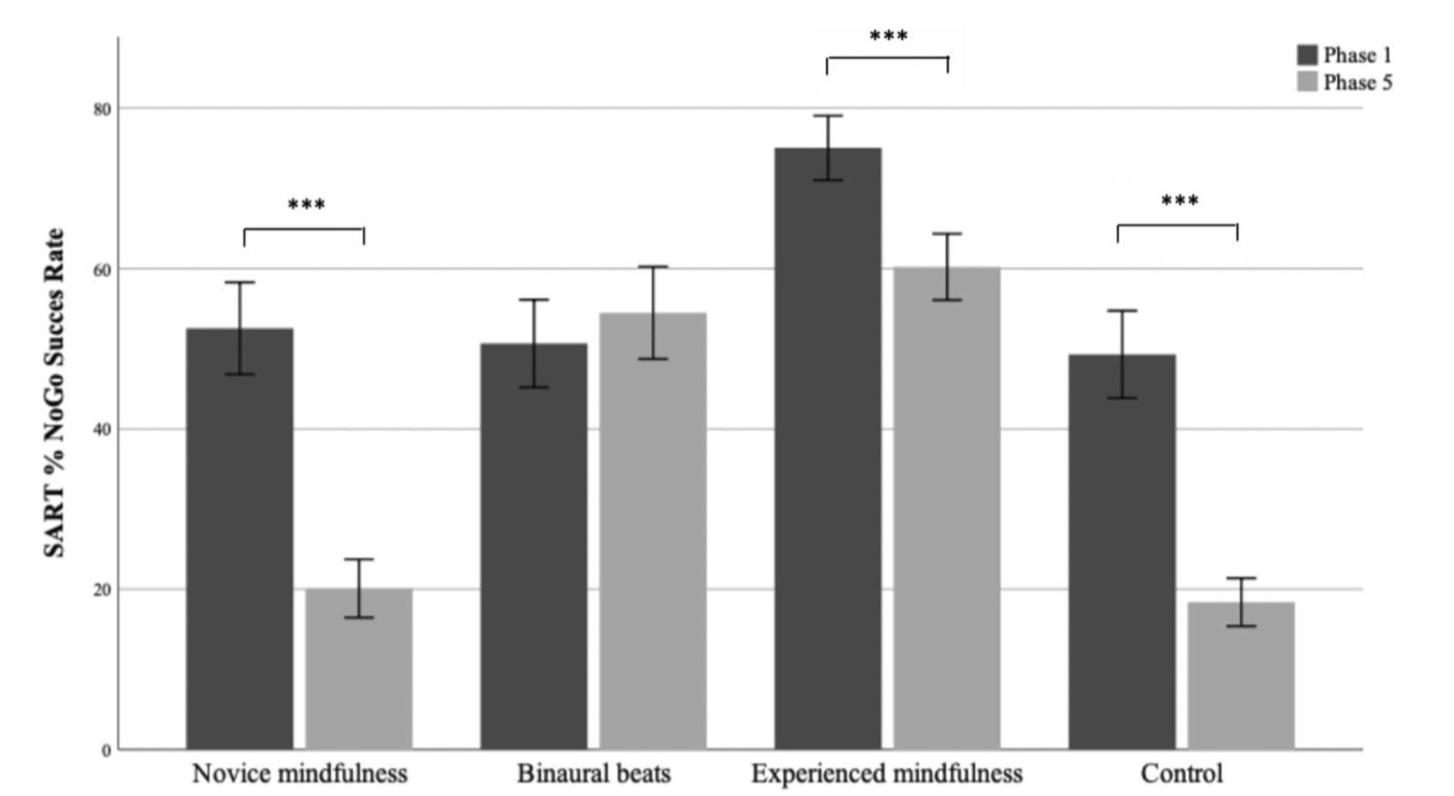
After 90 minutes of intense cognitive tasks, participants used different methods to recover: 14 Hz beta beats for 12 minutes, mindfulness meditation (experienced or novice), or quiet resting.
Key Findings:
14 Hz Beta beats: Performance improved from 50.7% to 54.5% (+3.8%)
Control group (quiet rest): Performance declined from 49.3% to 18.4% (-30.9%)
Novice mindfulness group: Significant decline from 52.6% to 20.1% (-32.5%)
Experienced mindfulness group: Moderate decline from 75.0% to 60.2% (-14.8%)
Beta beats provided immediate, substantial protection against cognitive fatigue.
Mindfulness benefits appeared only with extensive prior training. An interesting follow-up study would be combining mindfulness with binaural beats.
Try this specific frequency here:
Study 2: Long-Term Memory Improvement
Participants listened to either 20 Hz beta beats, 5 Hz theta beats, or white noise before memorizing a list of words.
Key Findings:
Beta beats increased word recall significantly:
Beta beats: 46% recall (27% relative improvement)
White noise: 36% recall
Theta beats: 35% recall
Recognition accuracy also improved with beta beats, but not theta.
Summary:
Beta beats specifically enhanced long-term memory and recognition of words compared to white noise.
Choosing the wrong frequency (theta) had no impact on memory, underscoring the importance of frequency selection.
Try this specific frequency here:
Practical Recommendations: How to Use Beta Beats Effectively
Memory Enhancement: Listen to 20 Hz beta beats during study or learning tasks. Aim to listen for 10 minutes before to “prime” your brain. Then listen throughout. The longer you listen, likely the more benefit there will be.
Fatigue Management: Take brief breaks using 14 Hz beta beats (about 12 minutes) during intense cognitive workloads. You can also try listening to this frequency during your tasks.
Choose Frequencies Carefully: Only beta-range frequencies (14-20 Hz) are supported by these studies.
Final Thoughts: Real Potential, Real Limitations
Binaural beats offer a surprisingly powerful boost to cognitive performance, especially given how accessible they are.
While they aren’t a substitute for foundational habits like quality sleep, regular breaks, and consistent mindfulness, the evidence shows they can deliver meaningful short-term gains in focus and attention. While more research is certainly needed, as a supplemental tool, they’re an easy, low-effort way to sharpen your mental edge exactly when you need it most.


What are the frequencies associated with Deep sleep (NOT REM) and any studies about beats and deep enhancement you are aware of?